Engaging and Motivating Students through Problem Based Learning
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centric learning methodology where the teacher acts as a facilitator and mentor, rather than a solution provider. Here, the teacher presents the student with a problem (not lectures) and the student discovers and works with content necessary to solve the problem. This allows the student to take ownership of his learning, apply course content, use technology meaningfully, and collaborate with others. It provides an opportunity to the student to examine what he knows, discover what he needs to learn and develop people skills for achieving higher performance in teams.
PBL is highly context-specific and presents the students with a real-world challenge similar to one they might encounter as a practitioner. The learning is experiential and the students learn the content as they try to address a problem. The goal is not to make students arrive at conclusion but to research the foundation upon which the solution is derived. There is emphasis on the process they used, options they considered, and the difficulties they encountered. The process involves convincing the team members with reason and reaching a consensus on how to proceed next.
PBL cultivates problem solving, critical thinking and collaborative skills which are necessary to manage in today’s rapidly changing environment.
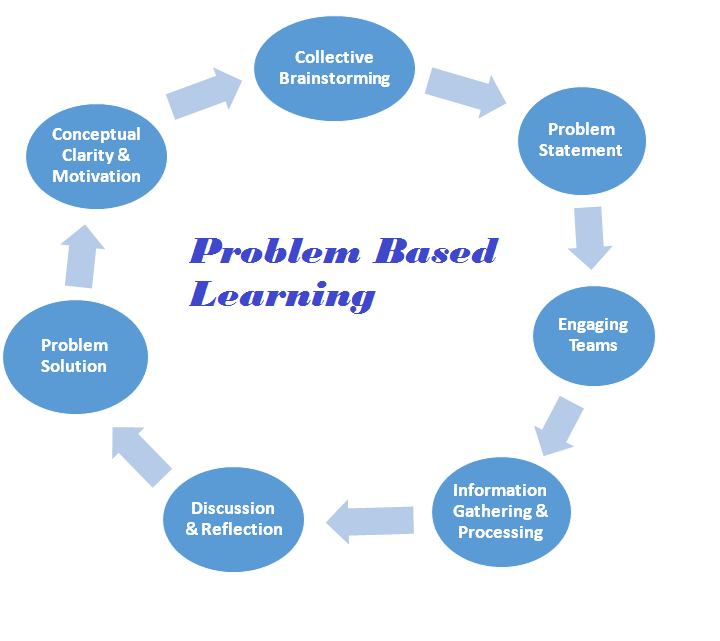
The PBL methodology is based on active, interactive, and collaborative learning. It involves the following steps:-
1. Collective Brainstorming
o discussing the problems/issues in a course/topic
o understanding the criticality
o exploring the critical problem
2. Problem Statement
o coming to a consensus on the problem to be worked upon
3. Engaging Teams
o clarifying roles
o utilising complementary skills
o promoting collaboration among team members
4. Information Gathering and Processing
o mapping already available information
o identifying the gaps
o collecting relevant information
o processing information collectively
5. Discussion and Reflection
o discussing alternative solutions
o reflecting on past experiences
o testing the alternatives with available knowledge
6. Problem Solution
o presenting the solution as a group
o supporting documents and evidence
7. Conceptual Clarity and Motivation
o teacher’s interventions
o usefulness of concepts to application
o discussion on course content
o willingness to learn more
As we can see from the above process, PBL places responsibility on the students’ shoulders for their own learning. Students take ownership of the process of learning and the outcome is also determined by the students themselves. This does not mean that the teacher abdicates her responsibility for determining what is important for students. The teacher, after brainstorming with the students, creates scenarios around real problems and presents it to the students to elicit the required thinking, discussion, research, and learning. Further, the teacher’s role is to pose self-reflective questions on students’ knowledge and assumptions.
The problems in PBL are typically in the form of cases, narratives of complex, real-world challenges common to the discipline being studied. For example, in an Organisational Behaviour course, concepts such as personality and perception, conflict and negotiation, communication, motivation, teamwork, leadership can easily be understood with the help of scenarios around real issues which the students have observed/experienced in their work, college or personal lives. Students also identify with problems related to stress management, time management, goal setting and work-life balance. There are no right or wrong answers to these problems; rather, there are reasonable solutions based on application of knowledge and skills.
This method gives teachers a sense of the level of intellectual maturity the students bring with them and allows them the opportunity to observe students’ learning processes. Students’ prior learning can greatly impact their current learning and often they surprise the teachers with their content and knowledge. Present generation students are flooded with information; however,they need the skills to locate the right resources, work in a team and synthesize relevant information to solve complex problems. PBL helps the students to realise their capabilities and increases their motivation to learn concepts through experiential learning. This learning has a lasting impact and enables the students to manage effectively under difficult circumstances.
Since the students are at the center of this method, it increases their willingness to participate and engage in the learning process and provides them with the necessary skills to deal with challenging situations; now and in their future careers.
_______________________________________________________________________________________