Abstract
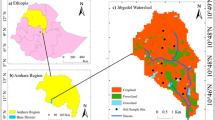
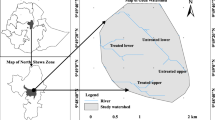
Land degradation such as declining soil fertility is the main cause for poverty in rural areas of developing countries due to reduced land productivity. To tackle the effect of soil degradation on agricultural production, soil and water conservation (SWC) measures such as bench terraces have been installed at large scale in Ethiopia highlands. However, the effects of such bench terraces on the evolution of selected soil properties are less studied. Thus, the overall objective of this study is to evaluate short-term effects of bench terraces on soil properties. Four terraced hillside farming sites and four adjacent control sites were purposely selected at Teshi, Ruba Feleg, Mechael Emba and Enda Chena of the Tigray region. For each selected site, three representative hillslope classes at foot slope, middle slope, and upslope positions were identified for soil sampling. Soil physico-chemical properties were analyzed using standard laboratory procedures at regional soil laboratory research center. The results revealed remarkable effects of bench terraces on rehabilitation of the degraded soils. However, its installation can also induce considerable negative impacts on soil fertility during the first few years due to soil translocation and exposure of subsoils. The results indicated that aggregate stability and soil pH values for most of the hillside farming sites have shown a significant difference (p ≤ 0.05) among upslope, middle and foot slopes positions and control sites which would be explained by erosion and leaching in the upslope and enrichment of base forming cations and clay at foot slope positions. High proportion of large aggregates size is observed at both Teshi and Ruba Feleg hillside farming sites compared to their corresponding control sites. The soil organic matter (SOM) content, total nitrogen (TN) and available phosphorous (Av.P) at Teshi site, TN at Ruba Feleg site, TN and Av.P at Michael Emba site and SOM and Av.P at Enda Chena hillside farming site are significantly different (p < 0.05) among the three slope classes of the sites and the corresponding control site. Moreover, mean SOM content and Av.P at Ruba Feleg site and SOM content at Michael Emba site have shown a significant difference (p < 0.05) among the three slope classes and the control sites except between upslope and middle slopes. Generally, the installation of bench terrace combined with soil fertility management practices such as application of organic manure and compost are important positive operation for changing most unproductive mountains and hillslopes into productive landscapes while contributing towards a sustainable land management in the area. This study provides important evidences on the effects of bench terraces on soil physical and chemical properties of the area to land managers and decision makers to aid sustainable land management practices in similar environments.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemayehu A (2007) Impact of terrace development and management on soil properties in Anjeni Area, West Gojam. Master’s thesis, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia
Andrew G, Williams J, Les T, Andy E, Marta G, Del T, Raoul B (1995) A field study of the influence of land management and soil properties on runoff and soil loss in central Spain. Environ Monit Assess 37(1–3):333–345
Asadi H, Raeisvandi A, Rabiei B, Ghadiri H (2010) Effect of land use and topography on soil properties and agronomic productivity on calcareous soils of a semi-arid region, Iran. Land Degrad Dev. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.1081
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Nitrogen total. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds), Methods of soil analysis, vol 2. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 95–624
Budry B, Curtis J (2007) Environmental perceptions and behavioral change of hillside farmers: the case of Haiti. J Caribb Agro-Econ Soc (CAES) 7(1):122–138
Cambardella CA, Elliott ET (1993) Carbon and nitrogen distribution in aggregates from cultivated and native grassland soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57(4):1071–1076
Chivenge PP, Murwira HK, Giller KE, Mapfumo P, Six J (2007) Long-term impact of reduced tillage and residue management on soil carbon stabilization: implications for conservation agriculture on contrasting soils. Soil Tillage Res 94:328–337
Descheemaeker K, Nyssen J, Rossi J, Poesen J, Haile M, Raes D, Muys B, Moeyersons J, Deckers J (2006) Sediment deposition and pedogenesis in exclosures in the Tigray highlands, Ethiopia. Geoderma 32:291–314
Etefa G, Frankl A, Zenebe A, Poesen J, Nyssen J (2017) Effects of check dams on runoff characteristics along gully reaches, the case of Northern Ethiopia. J Hydrol 545:299–309
Gebremedhin H, Gebresamual G, Abadi N, Hailemariam M, Teka T, Mesfin S (2017) Conversion of communal grazing land into arable land and its impacts on soil properties and vegetation cover. Arid Land Res Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/15324982.2017.1406412
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle size analysis: methods of soil analysis, 2nd edn. ASA-SSSA, Madison
Haile M, Herweg K, Stillhardt B (2006) Sustainable land management—a new approach to soil and water conservation in Ethiopia. Mekelle University, Mekelle
Haileslassie A, Priess J, Veldkamp E, Teketay D, Lesschen JP (2005) Assessment of soil nutrient depletion and its spatial variability on smallholders’ mixed farming systems in Ethiopia using partial versus full nutrient balances. Agricult Ecosyst Environ 108:1–16
Haregeweyn N, Poesen J, Nyssen J, Govers G, Verstraeten G, Vente J, Deckers J, Moeyersons J, Haile M (2008) Sediment yield variability in northern Ethiopia: a quantitative analysis of its controlling factors. Catena 75:65–76
Haregeweyn N, Tsunekawa A, Nyssen J, Poesen J, Tsubo M, Meshesha D, Brigitta S, Adgo E, Tegegne F (2015) Soil erosion and conservation in Ethiopia: a review. Progress in physical geography. In: Jackson ML 1958 Soil chemical analyses. Enllewood cliffs, New Jersey, pp 1–25
Jackson. ML (1958) Soil chemical analyses. Enllewood cliffs, New Jersey
Krahtopoulou A, Frederick C (2008) The stratigraphic implications of long term terrace agriculture in dynamic landscapes: polycyclic terracing from Kythera Island. Greece Geoarchaeol 23(4):550–585
Lasanta T, Arnaez J, Oserin M, Ortigosa LM (2001) Marginal lands and erosion in terraced fields in the Mediterranean mountains: a case study in the Camero Viejo (northwestern Iberian System, Spain). Mt Res Dev 21(1):69–76
Lema B, Kebede F, Mesfin S, Fitiwy I, Abraha Z (2016) Use of the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) for soil and nutrient loss estimation in long-used rainfed agricultural lands. North Ethiop Phys Geogr 37:3–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/02723646.2016.1198138 276–290
Lema B, Kebede F, Mesfin S, Fitiwy I, Abraha Z, Norgrove L (2017) Quantifying annual soil and nutrient lost by rill erosion in continuously used semiarid farmlands, North Ethiopia. Environ Earth Sci 76:190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6506-z
Mekuria W, Veldkamp E, Haile M, Nyssen J, Muys B, Gebrehiwot K (2007) Effectiveness of exclosures to restore degraded soils as a result of overgrazing in Tigray, Ethiopia. J Arid Environ 69:270–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2006.10.009
Mengel K, Kirby EA (1987) Principles of plant nutrition. Panima Publ. Corporation, New Delhi
Mesfin S, Taye G, Hailemariam M (2018) Effects of integrated soil and water conservation measures on soil aggregate stability, soil organic matter and soil organic carbon stock of smallholder farm lands in the semi-arid, northern Ethiopia. J Carbon Manag 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2018.1443641
Million A (2003) Characterization of indigenous stone bunding (Kab) and its effect on crop yield and soil productivity at Mesobit-Gedba, North Showa Zone of Amhara Region. Master’s thesis, Alemaya University, Ethiopia
Mulugeta D, Stahr K (2010) Assessment of integrated soil and water conservation measures on key soil properties in south Gondar, north-western highlands of Ethiopia. J Soil Sci Environ Manag 1(7):164–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-008-9157-8
Nyssen J, Vandenreyken H, Poesen J, Moeyersons J, Deckers J, Haile M, Salles C, Govers G (2005) Rainfall erosivity and variability in the Northern Ethiopian highlands. J Hydrol 311:172–178
Nyssen J, Poesen J, Desta G, Vancampenhout K, D’aes M, Yihdego G, Govers G, Leirs H, Moeyersons J, Naudts J, Haregeweyn N, Mitiku H, Deckers J (2007) Interdisciplinary on-site evaluation of stone bunds to control soil erosion on cropland in Northern Ethiopia. Soil Tillage Res 94:151–163
Nyssen J, Poesen J, Descheemaeker K, Haregeweyn N, Haile M, Moeyersons J, Deckers J (2008) Effects of region-wide soil and water conservation in semi-arid areas: the case of northern Ethiopia. Z Geomorph N F, 53, 291–315. https://doi.org/10.1127/0372-8854/2008/0052-0291
Olsen SR, Cole V, Watenable FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Cir. no. 939 analysis, part 2. Am Soc Agron 9:914–926
Peech M (1965) Hydrogen ion activity. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 914–926
Ramos MC, Cots-Folch R, Martinez-Casasnovas JA (2007) Sustainability of modem land terracing for vineyard plantation in a Mediterranean mountain environment the case of the Priorat region (NE Spain). Geomorphology 86(1–2):1–11
Siriri D, Tanya MM, Rousse T, Sake JK (2005) Crop and soil variability on terraces in the highlands of SW Uganda. Land Degrad Dev 16:569–579. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.688
Sodhi NS, Posa MRC, Lee TM, Bickford D, Koh LP, Brook BW (2009) The state and conservation of Southeast Asian biodiversity. J Biodivers Conserv. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-009-9607-5
Tadele A, Yihenew GS, Mitku H, Yamoh C (2011) Effect of soil and water conservation measures on selected soil physical and chemical properties and barley (Hordeum spp.) yield. J Environ Sci Eng 11:1483–1495
Tadele A, Terefe A, Selassie YG, Yitaferu B, Wolfgramm B, Hurni H (2013) Soil properties and crop yields along the terraces and topo-sequece of Anjeni watershed, Central Highlands of Ethiopia. J Agric Sci 5(2):134
Tadesse B, Mesfin S, Tesfay G, Abay F (2016) Effect of integrated soil bunds on key soil properties and soil carbon stock in semi-arid areas of northern Ethiopia. South Afr J Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1080/02571862.2016.1148788
Tarolli P, Preti F, Romano N (2014) Terraced landscapes: from an old best practice to a potential hazard for soil degradation due to land abandonment. Anthropog Publ Can Center Sci Educ 6:10–25
Taye G, Poesen J, Van Wesemael B, Vanmaercke M, Teka D, Deckers J, Haregeweyn N (2013) Effects of land use, slope gradient, and soil and water conservation structures on runoff and soil loss in semi-arid Northern Ethiopia. Phys Geogr 34:236–259
USDA (1998) Natural Resources Conservation Service, soil quality indicators: pH. Prepared by the National Soil Survey Center in cooperation with the Soil Quality Institute, NRCS, USDA, and the National Soil Tilth Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service. http://soils.usda.gov/sqi/publications/files/indicate.pdf
Vancampenhout K, Nyssen J, Gebremichael D, Deckers J, Poesen J, Haile M et al (2006) Stone bunds and soil conservation in the northern Ethiopian highlands: impacts on soil fertility and crop yield. Soil Tillage Res 90(1–2):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2005.08.004
Vanmaercke M, Zenebe A, Poesen J, Nyssen J, Verstraeten G, Deckers J (2010) Sediment dynamics and the role of flash floods in sediment export from medium-sized catchments: a case study from the semi-arid tropical highlands in northern Ethiopia. J Soils Sediments 10:611–627
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wang W, Chen WC, Wang KR, Xie XL, Yin CM, Chen AL (2011) Effects of long-term fertilization on the distribution of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in water-stable aggregates in paddy soil. Agric Sci China 10:1932–1940
Whalen JK, Chang C (2002) Macroaggregate characteristics in cultivated soils after 25 annual manure applications. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1637–1647
Yihenew G (2007) Evaluation of nitrogen and phosphorus as yield-limiting nutrients for maize grown on Alfisols of Western Amhara. Ethiop J Nat Resour 9(1):155–170
Zougmore RZ, Gnankambary S, Stroosnijedr LG (2002) Effects of stone lines on chemical characteristics, under continuous cropping in semiarid, Burkina Faso. Soil Tillage Res 66:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(02)00012-0
Acknowledgements
We thank Mekelle University for financial and material support for the research during data collection and analysis. Special thank also goes to the Tigray Agricultural Research Institute soil laboratory research center Mekelle branch for their cooperation and willingness for soil laboratory analysis. We thank local farmers and development agents (DA) of the studied hillslope farming sites for their time and cooperation during data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesfin, S., Taye, G., Desta, Y. et al. Short-term effects of bench terraces on selected soil physical and chemical properties: landscape improvement for hillside farming in semi-arid areas of northern Ethiopia. Environ Earth Sci 77, 399 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7528-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7528-x